ICD-10 Diagnosis Code for Family History of Pancreatic Cancer
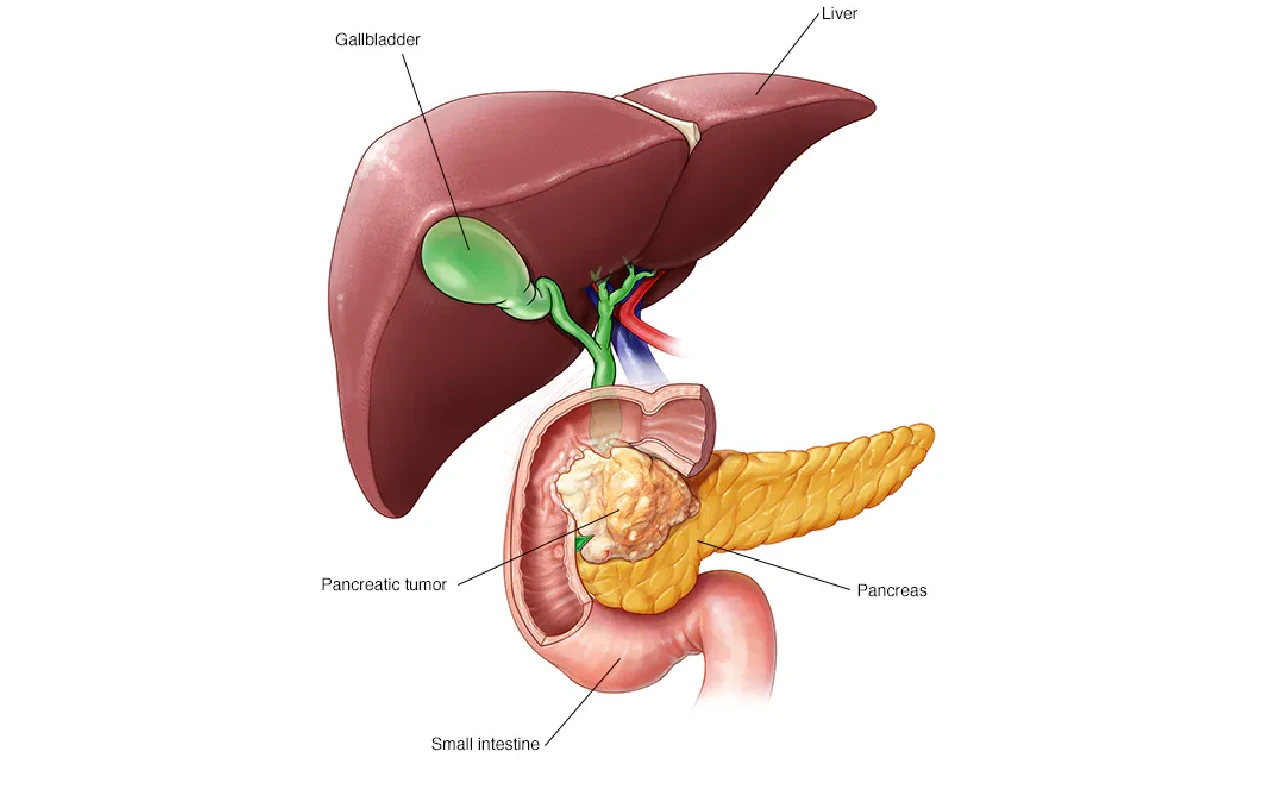
ICD-10 Diagnosis Code for Family History of Pancreatic Cancer – The icd-10 diagnosis code is key in medical coding, especially for family history of pancreatic cancer. It’s vital for tracking and analyzing health data. Healthcare providers use it to understand risks and prevent cancer.
Knowing the icd-10 code for pancreatic cancer is crucial for good patient care. This guide will cover everything about the icd-10 code for family history of pancreatic cancer. By using the right code, healthcare providers can document and bill accurately. This leads to better care for patients.
Understanding Family History of Pancreatic Cancer in Medical Coding
Family history is key in medical coding, especially for pancreatic cancer. It’s vital to record family cancer history accurately. This helps in risk assessment and prevention. Healthcare professionals can then offer better care and tailor treatment plans.
Importance of Documenting Family Cancer History
Recording family cancer history is crucial. It helps spot genetic risks early. This info also guides medical coding and ensures patients get the right care.
Role in Risk Assessment and Prevention
Knowing family history helps doctors gauge a patient’s risk of pancreatic cancer. This knowledge aids in creating personalized prevention plans. It includes screenings and surveillance.
Impact on Patient Care Planning
Family history greatly influences patient care, especially with a strong family history of pancreatic cancer. Healthcare teams can craft targeted treatment plans. These plans address the patient’s specific needs and risk factors.
| Family History | Medical Coding | Risk Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| First-degree relative with pancreatic cancer | Use specific ICD-10 codes to indicate family history | Increased risk of developing pancreatic cancer |
| Second-degree relative with pancreatic cancer | Use secondary codes to indicate family history | Moderate risk of developing pancreatic cancer |
Primary ICD-10 Diagnosis Code for Family History of Pancreatic Cancer
The primary icd-10 diagnosis code for family history of pancreatic cancer is key for accurate coding. It shows a patient’s family history of pancreatic cancer, a big risk factor. This code is vital for patient care and insurance claims.
When coding for family history of pancreatic cancer, the right primary code is crucial. It shows the patient’s relation to the family member with cancer, like parent, sibling, or child. Correct coding helps identify high-risk patients for early screening and care.
Some important points for coding family history of pancreatic cancer include:
- Using the correct icd-10 diagnosis code for family history of pancreatic cancer
- Indicating the patient’s relationship to the family member with pancreatic cancer
- Ensuring accurate and consistent coding to facilitate patient care and insurance claims
Clinical Documentation Requirements for Family Cancer History
Accurate and detailed clinical documentation is key for family cancer history. It involves collecting and recording important details. These include the type of cancer, the patient’s relationship to the affected family member, and the age of diagnosis. This information is crucial for assessing risk, preventing cancer, and planning patient care.
Family cancer history plays a big role in determining cancer risk. It’s vital to document this info accurately. The clinical documentation should include the patient’s family cancer history. This can be gathered through a detailed medical history and physical exam.
Essential Elements to Document
- Type of cancer
- Degree of relationship to the patient
- Age of diagnosis
- Any genetic testing or counseling that has been performed
It’s also important to be specific in clinical documentation. This means noting the exact type of cancer, like pancreatic cancer. It also includes the degree of relationship to the patient, such as first-degree or second-degree relative. Avoiding common errors like incomplete or wrong information is crucial. These mistakes can lead to wrong risk assessments and prevention plans.
By following these guidelines, healthcare providers can document family cancer history accurately. This is essential for delivering top-notch patient care. It helps identify those at high risk of cancer, allowing for early action and prevention. Good clinical documentation is key to meeting these requirements and ensuring the best care for patients.
Related ICD-10 Codes and Classifications
When documenting a family history of pancreatic cancer, it’s crucial to use the right icd-10 codes and classifications. These codes help doctors understand the patient’s risk factors. They also help in creating a good treatment plan. Related codes might include those for other cancers, like breast or ovarian cancer, which could be part of the patient’s family history.
Doctors might also use other classifications to document the patient’s medical history. These classifications can include codes for genetic disorders or other health conditions. These could be linked to the patient’s cancer risk. Some examples of related icd-10 codes and classifications include:
- Codes for other types of cancer, such as Z85.46 (Personal history of malignant neoplasm of breast)
- Codes for genetic disorders, such as Z82.49 (Family history of other genetic disorders)
- Codes for other health conditions, such as K86.1 (Chronic pancreatitis)
By using the correct icd-10 codes and classifications, doctors can ensure accurate documentation and billing. They can also provide better care for patients with a family history of pancreatic cancer.
Using Family History Codes in Different Healthcare Settings
Family history codes are key in many healthcare areas, like outpatient care. They help doctors see if a patient might get sick, like pancreatic cancer. This way, they can start early treatments.
In places like clinics, these codes help doctors decide how to treat patients. For example, someone with a family history of pancreatic cancer might need more tests. This ensures each patient gets care that fits their needs.
Outpatient Documentation Guidelines
Guidelines for outpatient care stress the need for accurate family history coding. Doctors should write down a patient’s disease history, who they’re related to, and when they got sick. This helps doctors know how to best help the patient.
Preventive Care Scenarios
Family history codes are also used for preventive care, like screenings. For instance, someone with a family history of pancreatic cancer might get checked more often. Doctors use these codes to figure out who needs extra care and give them the right advice.
| Healthcare Setting | Use of Family History Codes |
|---|---|
| Outpatient | Guide treatment decisions and preventive care measures |
| Inpatient | Inform diagnosis and treatment plans |
| Specialist Referral | Provide context for referral and guide specialist care |
Using family history codes in healthcare, like in clinics, helps doctors give better care. It helps prevent diseases and makes patients healthier.
Code Combination and Sequencing Rules
Understanding icd-10 codes is key. Code combination means picking the best codes for a patient’s diagnosis. For family history of pancreatic cancer, this might include codes for the patient’s relation and the cancer type.
The sequencing rules tell us how to order these codes. The main diagnosis comes first, followed by secondary ones. For family history, the cancer code (Z80.0) comes after the patient’s current diagnosis.
Important things to remember include:
- Choose the most accurate codes for the patient’s condition
- Use codes to show the patient’s relation to the family member with cancer
- Follow the sequencing rules to list codes correctly
- Use secondary codes for related or additional diagnoses
By following these rules, healthcare providers can code accurately for patients with a family history of pancreatic cancer. This ensures the right icd-10 codes are used.
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|
| Z80.0 | Family history of malignant neoplasm of pancreas |
| C25.0 | Malignant neoplasm of head of pancreas |
| C25.1 | Malignant neoplasm of body of pancreas |
| C25.2 | Malignant neoplasm of tail of pancreas |
Risk Assessment and Screening Recommendations
People with a family history of pancreatic cancer face a higher risk. It’s crucial to do a thorough risk assessment. This looks at medical and family history, and other risk factors.
Genetic counseling is a key part of this process. It involves talking to a genetic counselor about your risk. They can help you understand your risk and make health decisions.
Genetic Counseling Considerations
Genetic counseling is vital. It covers your family and medical history. A counselor can help you understand your risk and plan for it.
Surveillance Guidelines
High-risk individuals need regular checks. This might include MRI or CT scans. The type of screening depends on your risk and health history.
Prevention Strategies
There’s no sure way to prevent pancreatic cancer. But, you can lower your risk. Stay healthy, exercise, and avoid tobacco. Eating lots of fruits and veggies can also help.
By following screening advice and reducing risk, you can be proactive about your health. Regular risk assessments and genetic counseling help you make informed health choices.
Moving Forward: Implementing Accurate Family History Documentation in Practice
It’s key to document a patient’s family history of pancreatic cancer well. This helps in assessing risks, preventive care, and tailoring treatments. Healthcare pros need to make family history recording a big part of their work. This way, we can make sure the ICD-10 codes match the patient’s history, leading to better care.
Healthcare groups should teach staff about the value of family history records. They should learn about ICD-10 codes and how to record this info right. Also, using electronic health records (EHRs) can make it easier and keep records consistent.
By recording family history of pancreatic cancer well and using the right ICD-10 codes, we gain insights. This helps in managing health populations, guiding genetic counseling, and helping patients detect and prevent early. Working together, we can improve patient care and help fight this tough disease.