ICD 10 Code for Pancreatic Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
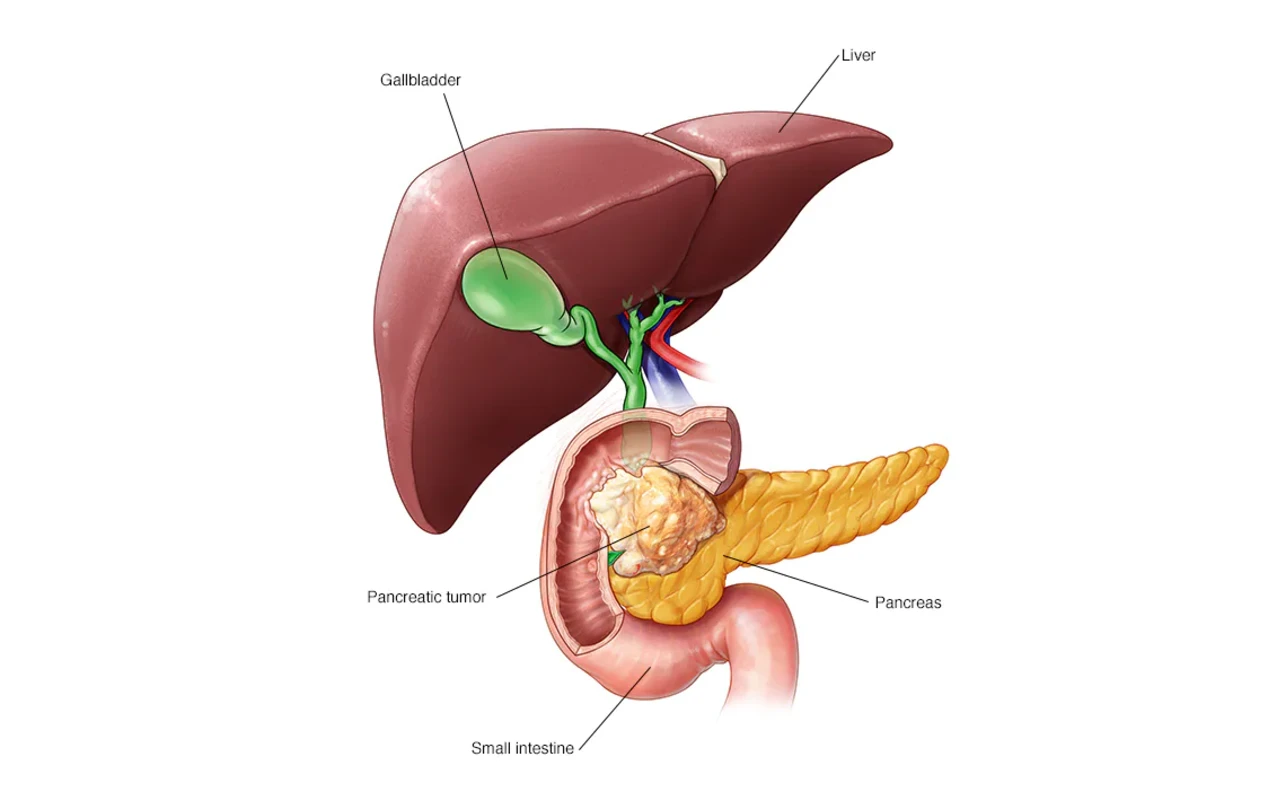
Pancreatic cancer is a serious and often life-threatening condition that affects thousands of individuals worldwide each year. Its impact on patients and their families cannot be overstated, as it often presents late, making early detection crucial. Medical professionals rely on coding systems like the ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision) to classify and manage such conditions effectively.
If you’re a medical coder, healthcare provider, or someone navigating the complexities of a pancreatic cancer diagnosis, understanding the ICD 10 code for pancreatic cancer is essential. This article provides an in-depth look at the ICD-10 codes related to pancreatic cancer, their importance, and how they streamline the healthcare process.
What Is the ICD-10 Code for Pancreatic Cancer?
The primary ICD-10 code for pancreatic cancer is C25, representing malignant neoplasms of the pancreas. This category is further divided into subcategories based on the specific location within the pancreas, ensuring precise diagnosis and treatment planning.
ICD-10 Code Breakdown: Understanding C25
To decode C25, let’s look at its structure:
- C: Indicates a malignant neoplasm.
- 25: Represents the pancreas as the affected organ.
This simplicity makes the ICD-10 system efficient for recording and analyzing pancreatic cancer cases.
Subcategories of C25: Detailed Breakdown
The pancreas consists of different regions, and ICD-10 subcategories provide further specificity:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| C25.0 | Malignant neoplasm of head of pancreas |
| C25.1 | Malignant neoplasm of body of pancreas |
| C25.2 | Malignant neoplasm of tail of pancreas |
| C25.3 | Malignant neoplasm of pancreatic duct |
| C25.4 | Malignant neoplasm of endocrine pancreas |
| C25.7 | Malignant neoplasm of other parts of pancreas |
| C25.8 | Malignant neoplasm of overlapping sites of pancreas |
| C25.9 | Malignant neoplasm of pancreas, unspecified |
Selecting the most accurate subcategory ensures precise medical documentation and billing.
Why Is the ICD-10 Code Important?
1. Improved Communication
ICD-10 codes provide a standardized language for healthcare professionals, ensuring everyone involved in patient care is on the same page.
2. Accurate Billing
Insurance companies use ICD-10 codes to process claims efficiently. Proper coding guarantees that patients receive the coverage they deserve.
3. Epidemiological Insights
Public health agencies use these codes to track pancreatic cancer trends, identify risk factors, and allocate resources for prevention and treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer
Common Symptoms
Pancreatic cancer is notorious for being asymptomatic in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
Diagnostic Procedures
- Imaging Tests: CT scans, MRIs, and endoscopic ultrasounds help visualize the pancreas.
- Blood Tests: Elevated CA-19-9 levels may indicate pancreatic cancer.
- Biopsy: Confirms malignancy by examining tissue samples.
Commonly Associated ICD-10 Codes
In many cases, pancreatic cancer is associated with additional conditions or complications. Below are some relevant ICD-10 codes:
| Code | Condition |
| C77.2 | Secondary malignant neoplasm of regional lymph nodes |
| C78.6 | Secondary malignant neoplasm of retroperitoneum and peritoneum |
| R16.2 | Hepatomegaly with splenomegaly, not elsewhere classified |
| K86.1 | Chronic pancreatitis |
| Z85.07 | Personal history of malignant neoplasm of pancreas |
These codes complement C25 and provide a holistic view of a patient’s condition.
Treatment Options for Pancreatic Cancer
1. Surgery
- Whipple Procedure: Removes the head of the pancreas, part of the small intestine, and other structures.
- Distal Pancreatectomy: Removes the tail and body of the pancreas.
2. Chemotherapy
Often used after surgery or as a standalone treatment for advanced cases.
3. Radiation Therapy
Targets cancer cells with high-energy beams, often combined with chemotherapy.
4. Targeted Therapy
Focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth, offering a more personalized treatment approach.
How to Use ICD-10 Codes Effectively
1. Ensure Diagnostic Accuracy
Accurate diagnosis is critical for selecting the right ICD-10 code. Imaging and biopsy results should support the documentation.
2. Choose Specific Codes
Always opt for the most specific subcategory (e.g., C25.1 for the body of the pancreas) to reflect the exact diagnosis.
3. Keep Documentation Detailed
Include details about the cancer’s stage, location, and any metastasis in medical records.
4. Stay Informed
ICD-10 codes are updated regularly. Keeping up with changes ensures compliance and accuracy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the ICD-10 code for metastatic pancreatic cancer?
The appropriate code depends on the location of the metastasis. For instance, C78.6 is used for secondary malignant neoplasms in the retroperitoneum and peritoneum.
2. Are ICD-10 codes universal?
Yes, ICD-10 codes are used globally, although some countries have minor adaptations for their healthcare systems.
3. Can pancreatic cancer have multiple ICD-10 codes?
Yes, a patient’s condition may require multiple codes to reflect primary cancer, metastases, and associated complications.
Conclusion
Understanding the ICD 10 code for pancreatic cancer is vital for healthcare providers, coders, and patients alike. The primary code, C25, along with its subcategories and related codes, ensures accurate documentation, effective communication, and streamlined healthcare processes. From diagnosis to treatment planning and insurance claims, ICD-10 codes play a pivotal role in managing pancreatic cancer.
Read more: