Describe 3 Reasons Why Cells Can Form Tumors
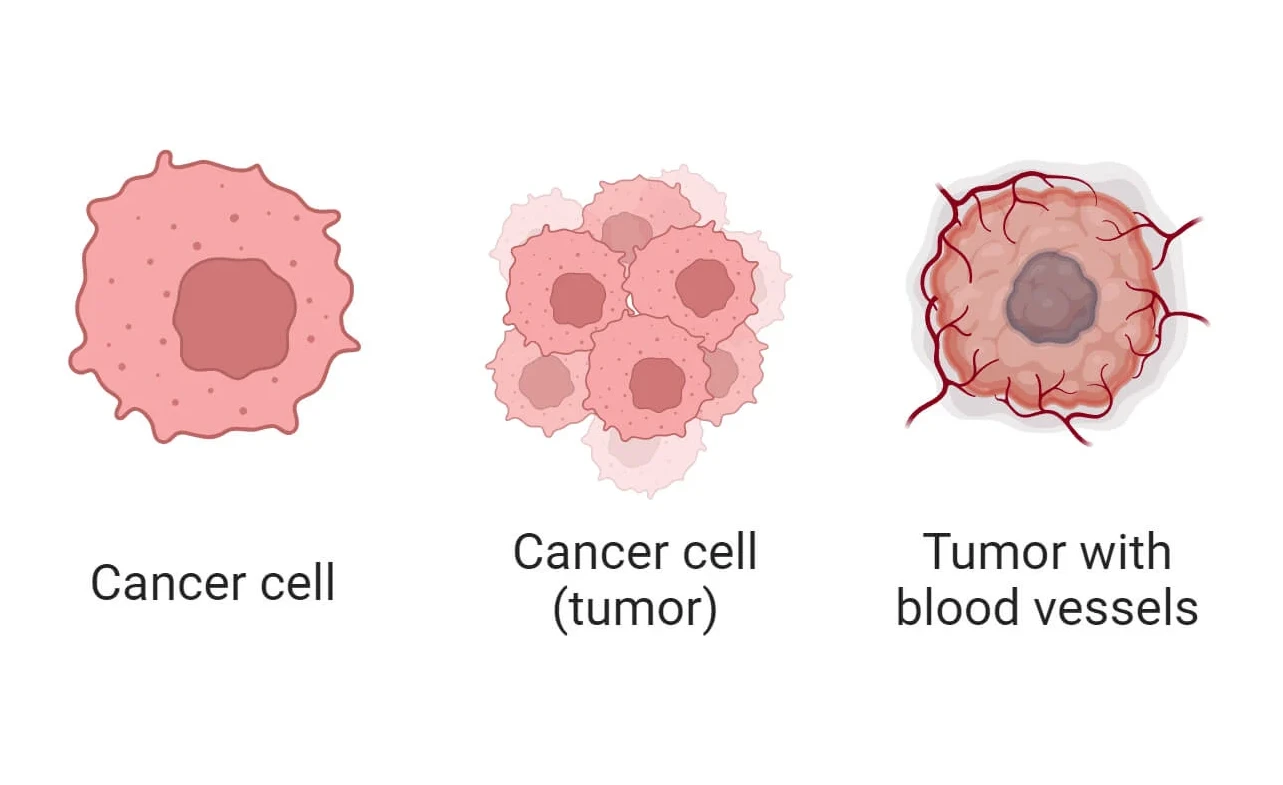
Describe 3 Reasons Why Cells Can Form Tumors – Cancer happens when cells in our body grow and divide without control. This can be caused by genetic changes, environmental factors, or cell behavior issues. Knowing why tumors form is key to fighting cancer.
Cells can turn into tumors for several reasons. These include uncontrolled growth, genetic damage, and problems with cell death. These factors are important to understand. They help us find better ways to prevent and treat cancer.
Understanding Normal Cell Behavior and Development
Normal cell function is key to keeping our bodies healthy. Cells grow, divide, and die in a controlled way. Knowing how healthy cells work helps us understand cell behavior and development.
In our bodies, cells are the basic building blocks of life. Their behavior is carefully managed to keep them functioning right. The process of cell division, or mitosis, lets cells make copies of themselves. This is important for growth, fixing damaged tissues, and keeping our bodies in good shape.
Key Aspects of Normal Cell Behavior
- Cell growth and division are regulated by a complex system of signals and pathways.
- Cells have a built-in mechanism for repairing damaged DNA to prevent mutations.
- Normal cell function is maintained through a delicate balance of cell growth, division, and death.
Having regular growth control is crucial to stop cells from growing too much. This can lead to tumors. The way cells behave and function is closely tied. Any disruption can have serious effects on our health. By understanding normal cell behavior, we can see the importance of keeping cells in balance.
| Cell Behavior Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Cell Growth Regulation | Prevents uncontrolled cell growth |
| Cell Division Regulation | Maintains tissue homeostasis |
| DNA Repair Mechanisms | Prevents genetic mutations |
What Defines a Tumor and How It Differs from Normal Tissue
A tumor is a mass of tissue that forms when cells grow and divide too much. Or when they don’t die when they should. This can happen due to genetic mutations or environmental factors.
Tumors can be either benign or malignant. Benign tumors are non-cancerous and don’t spread. Malignant tumors are cancerous and can spread to other parts of the body. Tumor cells have a few key traits:
- They grow and divide without control.
- They can invade surrounding tissues.
- They can spread to other parts of the body.
- They resist normal cell death mechanisms.
Knowing what a tumor is and how tumor cells behave is key. It helps in early detection and treatment. By spotting abnormal cell growth early, people can prevent tumors and get medical help if needed.
| Tumor Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Benign | Non-cancerous, does not spread |
| Malignant | Cancerous, can invade and spread |
Describe 3 Reasons Why Cells Can Form Tumors
Cells can form tumors for many reasons. Genetic changes and problems with growth signals are key. When cells mutate, they can’t control how they grow and divide.
There are three main reasons cells can form tumors. These include:
- DNA damage and genetic mutations, which can happen from the environment or DNA copying mistakes
- Disruptions in growth signaling pathways, causing cells to grow and divide too much
- Failure of natural cell death mechanisms, letting damaged cells live and get more mutations
DNA Damage and Genetic Mutations
DNA damage and genetic mutations can come from many sources. This damage can make cells grow out of control and form tumors. These mutations can mess with genes that control growth, making tumors worse.
Disruption of Growth Signaling Pathways
Growth signaling pathways are important for controlling cell growth and division. When these pathways get disrupted, cells can grow too much. This can lead to tumors. Genetic mutations can mess with these pathways, helping tumors grow.
Failure of Natural Cell Death Mechanisms
Natural cell death, like apoptosis, helps get rid of damaged cells. If this doesn’t work, damaged cells can keep living and getting more mutations. This can lead to tumors. Understanding how tumors form, including genetic changes and growth pathway problems, is key to fighting cancer.
| Reason | Description |
|---|---|
| DNA damage and genetic mutations | Genetic mutations can disrupt normal cellular function, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and tumor formation |
| Disruption of growth signaling pathways | Disruptions in growth signaling pathways can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation, contributing to tumor formation |
| Failure of natural cell death mechanisms | Failure of natural cell death mechanisms can allow damaged cells to survive and accumulate further mutations, contributing to tumor formation |
Environmental Factors That Trigger Tumor Formation
Environmental factors are key in starting tumor growth. They include chemicals, physical, and biological agents. Being exposed to these can raise the chance of tumors. For example, carcinogens, which are cancer-causing substances, are found in many places.
Chemical carcinogens, radiation, and viruses and bacteria are common causes. They damage DNA, leading to genetic changes and tumors. Knowing these factors and how to avoid them is important.
Chemical Carcinogens in Daily Life
Chemical carcinogens are everywhere, in food, water, and air. Pesticides, heavy metals, and industrial pollutants are examples. They can be swallowed, breathed in, or absorbed through the skin, raising tumor risks.
Radiation Exposure Risks
Radiation is another factor that can lead to tumors. Sources include UV rays, X-rays, and gamma rays. Long-term exposure can harm DNA, leading to mutations and tumor risk.
Viral and Bacterial Influences
Viruses and bacteria can also cause tumors. Viruses like HPV can lead to cancer, and bacteria like Helicobacter pylori can increase stomach cancer risk. Knowing about carcinogens helps prevent tumors and lower cancer risk.
| Environmental Factor | Example | Risk of Tumor Formation |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Carcinogens | Pesticides, heavy metals | High |
| Radiation Exposure | UV rays, X-rays | Medium |
| Viral and Bacterial Influences | HPV, Helicobacter pylori | High |
The Role of the Immune System in Tumor Development
The immune system is key in stopping tumor development. It finds and fights tumor cells. A strong immune system can spot and get rid of abnormal cells before they grow into tumors.
There are several ways the immune system can spot tumor cells, including:
- Identifying abnormal cell surface proteins
- Recognizing tumor-specific antigens
- Responding to inflammation and tissue damage
The immune system also attacks these cells. It uses immune cells like T cells and natural killer cells. Having a strong immune system helps prevent tumor development and lowers cancer risk.
Early Warning Signs and Risk Factors
It’s important to know the early signs and risk factors for tumors. This knowledge helps get medical help quickly and start treatment early. Tumors can show up in different ways. Spotting these signs early can make a big difference.
There are many things that can increase your chance of getting a tumor. These include your genes, the environment, and your lifestyle. Knowing these risk factors can help you take steps to lower your risk. For example, staying away from harmful chemicals and radiation can help.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Persistent fatigue or weakness
- Changes in skin pigmentation or new growths
- Unusual bleeding or discharge
High-Risk Populations
Some people are more likely to get tumors because of their genes or environment. This includes those with a family history of cancer, people exposed to harmful substances, and those with weak immune systems.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice any of these symptoms or are at high risk, see a doctor right away. Early treatment can greatly improve your chances of a good outcome.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic Predisposition | Family history of cancer or genetic mutations |
| Environmental Factors | Exposure to chemical carcinogens or radiation |
| Lifestyle Choices | Unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, or tobacco use |
Taking Control: Prevention and Proactive Measures
While tumors might seem scary, there are steps you can take to lower your risk. Eating well, exercising regularly, and avoiding harmful substances are key. Also, getting regular health checks can help catch problems early.
By being informed and proactive, you can manage your health better. This way, we can all live healthier lives with less risk of cancer.
Baca juga: