Can Constant Itch in the Groin Area Be Cancer?
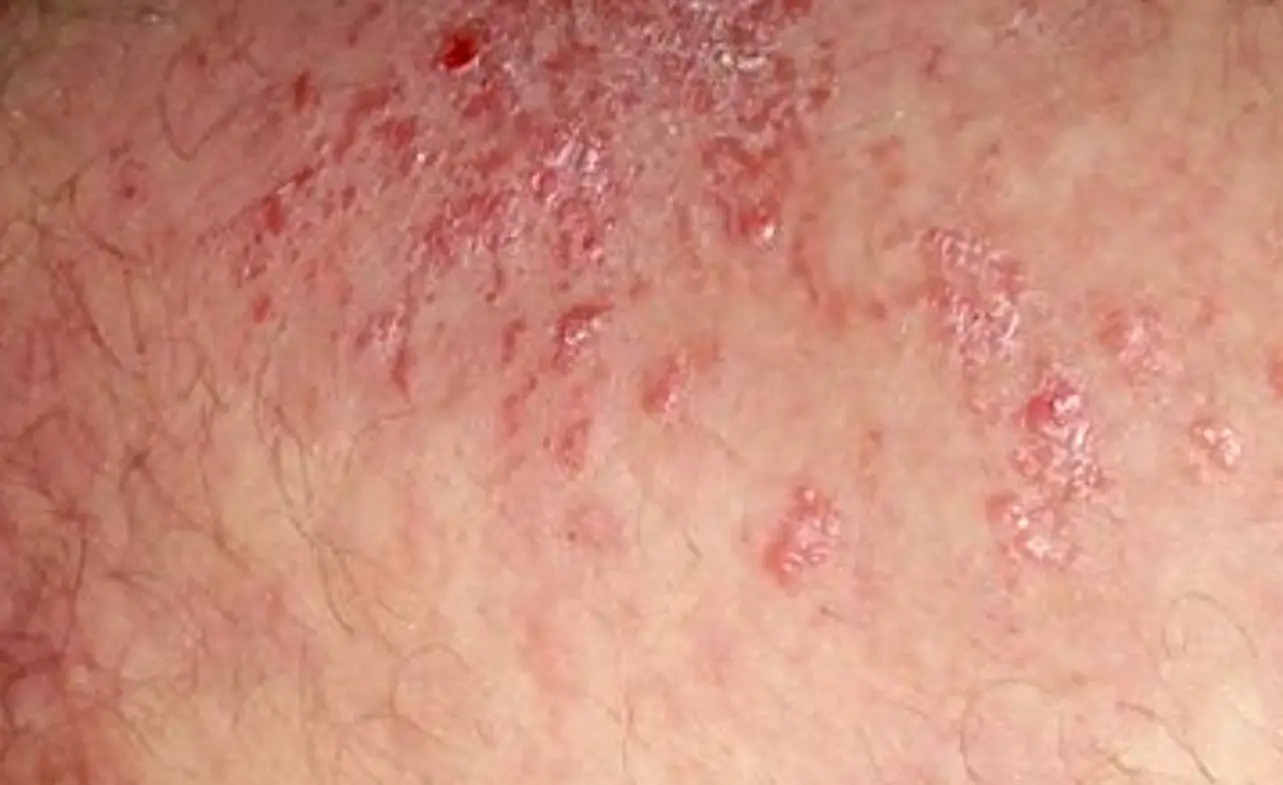
Experiencing an itch in the groin area can be uncomfortable and frustrating, leading many to wonder if it could indicate a serious underlying condition like cancer. While itching in this area is often caused by more common and less severe conditions, it’s essential to understand the potential causes, symptoms, and when to seek medical advice.
This article explores the connection between persistent groin itching and cancer, provides insights into common causes, and discusses how to address the issue effectively. Let’s delve deeper into this topic and separate facts from misconceptions.
What Causes Constant Itching in the Groin Area?
H2: Common Non-Cancerous Causes
Persistent itching in the groin area is usually associated with benign conditions, such as:
- Fungal Infections (Jock Itch): Caused by a fungal overgrowth, jock itch typically results in red, itchy patches of skin in the groin.
- Eczema or Dermatitis: Skin conditions like eczema can cause chronic itching and irritation.
- Allergic Reactions: Reactions to laundry detergents, soaps, or clothing materials may trigger itching.
- Poor Hygiene: Accumulation of sweat and bacteria can lead to skin irritation and discomfort.
While these conditions are not life-threatening, they can significantly impact daily life if left untreated.
H3: Could It Be Cancer?
Although rare, constant itching in the groin area can sometimes be a symptom of certain cancers. The most notable ones include:
- Skin Cancer: Persistent itching in a localized area could indicate skin cancer, such as squamous cell carcinoma or melanoma. These conditions may present as non-healing sores, unusual moles, or scaly patches.
- Lymphoma: Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma can cause generalized itching, including in the groin. This is often accompanied by swollen lymph nodes and night sweats.
- Penile or Vulvar Cancer: In rare cases, itching could be an early sign of penile or vulvar cancer, often accompanied by lesions or discoloration in the affected area.
Recognizing Warning Signs
H2: When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional if the following symptoms accompany the itching:
- Persistent Itching: If itching lasts longer than two weeks despite proper hygiene and over-the-counter treatments.
- Visible Changes: The presence of lumps, sores, discoloration, or thickened skin in the groin.
- Systemic Symptoms: Unexplained weight loss, fever, night sweats, or swollen lymph nodes.
H3: Differentiating Benign from Serious Causes
While most causes of groin itching are benign, cancers often have additional warning signs. Keeping track of accompanying symptoms can help in early diagnosis and treatment.
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Red, flaky patches | Fungal infection |
| Unusual lumps or sores | Skin or penile cancer |
| Generalized itching | Lymphoma |
| Burning sensation | Allergic reaction |
How Is Groin Itching Diagnosed?
H2: Medical Examination
When you visit a healthcare provider, they may perform:
- Physical Exam: A thorough examination of the affected area to look for visible signs of infection or lesions.
- Skin Biopsy: If cancer is suspected, a small sample of skin may be taken for analysis.
- Blood Tests: To check for systemic conditions like lymphoma.
H3: Imaging Tests
If swollen lymph nodes or deeper tissue issues are involved, imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI may be used to rule out serious conditions.
Treatments for Groin Itching
H2: Managing Non-Cancerous Conditions
Most cases of groin itching can be treated effectively with the following approaches:
- Antifungal Creams: For fungal infections like jock itch.
- Moisturizers: To soothe eczema or dermatitis.
- Antihistamines: To alleviate itching caused by allergies.
- Improved Hygiene: Regular cleaning and drying of the groin area to prevent bacterial buildup.
H3: Treating Cancer-Related Itching
If cancer is diagnosed as the underlying cause, treatment options may include:
- Surgery: To remove cancerous growths.
- Radiation or Chemotherapy: For systemic cancers like lymphoma.
- Targeted Therapies: Depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Preventing Groin Itching
H2: Lifestyle Changes
Preventing groin itching often comes down to maintaining healthy habits:
- Wear Breathable Fabrics: Opt for cotton underwear to reduce moisture.
- Use Gentle Products: Avoid harsh soaps or detergents that may irritate the skin.
- Stay Hydrated: Keeping your skin hydrated can prevent dryness and itching.
- Protect Against Infections: Avoid sharing personal items like towels and practice safe hygiene.
H3: Regular Check-Ups
Routine health screenings and self-checks can catch potential problems early. If you notice any unusual changes, consult your healthcare provider promptly.
Conclusion
Constant itching in the groin area is usually linked to common and treatable conditions, such as fungal infections or allergies. However, in rare cases, it may signal a more serious condition, including certain types of cancer. Paying attention to accompanying symptoms and seeking timely medical advice is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding the causes of groin itching empowers you to take proactive steps toward maintaining your health. If you’re experiencing persistent symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional to ensure peace of mind and well-being.
Read more: